Are you looking to make your own SCADA system using Omron PLC? In this detailed guide, we’ll walk you through the core concepts of Omron PLC communication using the FINS protocol, and how you can create a fully functional SCADA system using VB.NET and Visual Studio. Whether you’re a beginner or an automation professional, this tutorial is designed to help you get started quickly.
What This Post Covers
- Introduction to Omron PLC communication
- Understanding the FINS protocol
- Command and response frame structure
- Memory area write syntax
- Sample code using VB.NET
- Free SCADA project download
✅ Download Sample Project Here
✅ Download Manuals from Omron Official Website
Introduction to Omron PLC Communication with FINS
Omron PLCs communicate over Ethernet using a protocol called FINS (Factory Interface Network Service). This allows your SCADA application to perform operations like reading and writing memory values without altering the PLC’s main ladder logic program.
The FINS communication service works over a dedicated UDP/IP port and is structured around sending command frames and receiving response frames. Each frame includes:
- A FINS Header (transfer control info)
- A Command Field (read/write instruction)
- A Parameter/Data Field (memory addresses, values, etc.)
Before building your SCADA system, it’s essential to understand this frame format.
Understanding FINS Command Frames
FINS SEND Command Frame – Example
📷 Image 1: FINS SEND Command Frame

Each SEND frame sent to the PLC results in a response with a response code, added to the beginning of the FINS parameter/data field.
📷 Image 2: FINS Response Code Structure


📷 Image 3: Example FINS Response

FINS Frame Parameter Breakdown
Here’s a quick explanation of each part of the FINS frame, which you’ll use in your SCADA interface.
Key Parameters:
- RSV (Reserved): Always set to
00(Hex) - GCT (Gateway Count): Usually
02(Hex) - DNA (Destination Network Address):
00for local, or01–7Ffor remote networks - DA1 (Destination Node Address): Node number (not the IP address)
- DA2 (Destination Unit Address): Typically
00for CPU - SNA, SA1, SA2: Source equivalents of the above
- SID (Service ID): Unique identifier to match responses
📷 Image 5: Parameter Example

Memory Area Codes in Omron PLC
To write to a memory area, you must know its code. Here’s an overview:
| Code (Hex) | Memory Area |
|---|---|
30 | CIO (Control I/O) |
82 | DM (Data Memory) |
B0 | HR (Holding Relay) |
B1 | AR (Auxiliary Relay) |

Example FINS Command in VB.NET
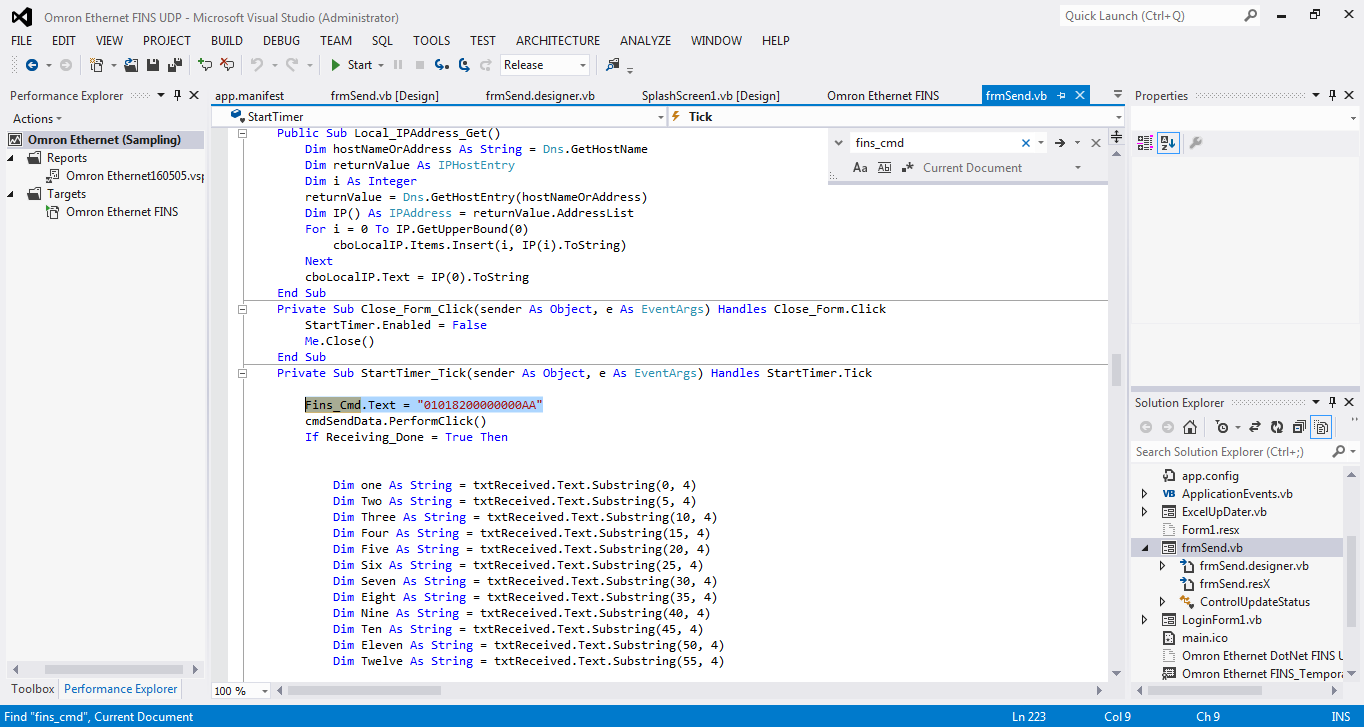
Let’s look at an example where a tag Fins_Cmd_Text = "010230000A00000101" is used to send a memory write command.
Breakdown of "010230000A00000101":
0102→ Memory Area Write Command3000→ Memory Type (CIO)000A00→ Start Address0001→ Number of Elements01→ Value to Write

VB.NET Configuration Snippet
RemoteIPAddress.Text = "192.168.250.1"
ICF = "80"
GCT = "03"
RSV = "00"
SID = "00"
SNA1.Text = "00"
SA11.Text = "64"
SA21.Text = "00"
DNA1.Text = "00"
DA11.Text = "00"
DA21.Text = "00"
This code sets up your application to send properly structured FINS commands to an Omron PLC over Ethernet.



Make Your Own SCADA with Omron PLC and VB.NET
With the right knowledge of Omron PLC communication and some basic VB.NET coding skills, you can develop your own SCADA interface. You’ll be able to:
- Monitor real-time PLC data
- Control outputs from your PC
- Log and visualize industrial processes
- Customize dashboards for any automation task
Get Started Now
✅ Download the Sample Project (VB.NET + Omron FINS)
📚 Download Omron PLC Manuals from the Official Site
Creating your own SCADA system with Omron PLC communication is completely achievable—even if you’re just starting out. With a solid understanding of FINS protocol and memory mapping, you can create a reliable and scalable SCADA application for industrial automation.
Have any questions or want to share your project? Feel free to reach out or leave a comment!

